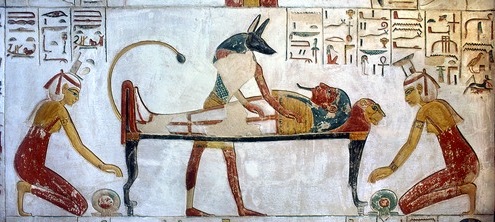
Ancient Egypt iconography is usually clear and understandable. Some other times, although the scenes are explicit, the sense of the image it is not so clear. That happens especially with religious images accompanying sacred texts from XIX Dynasty. That is the case of the resurrection scene from the tomb of Ramses IX belonging to the Book of the Caverns, in which four women pull their front lock of hair towards the mummy.

Women pulling lock of hair over the dead. Tomb of Ramses IX. Valley of the Kings. XX Dynasty. Photo: Mª Rosa Valdesogo Martín.
We know that this was a gesture made by mourners as one of the practices for helping in the dead’s restoration. But we also know tha these mourners making that were the two representatives of Isis and Nephtys.
The scene from the tomb of Ramses IX shows four women instead of two. Now the question is why?

Four mourners for Osiris with their front lock of hair falling forwards. Temple of Abydos. Photo: Mª Rosa Valdesogo Martín
Looking for more exmaples the only similar scene we found is an image from the temple of Osiris in Abydos. Here four women appear in a sorrow position with a front lock of hair falling forwards. Although they are not pulling the hair, it is clear the realtionship of it with the Osiris resurrection. But the inportant point here is that they are four and not two.
In the Egyptian Book of the Caverns from the tomb of Ramses IX, these four women are named as “...the Goddesses who mourn together in the secret place of Osiris…“. So, it would not be crazy to think about these four female figures in the temple of Osiris in Abydos, also as women with a divine nature.
But…who?…Any idea?…
We will see in the next post.