The word s3mt appears repeatedly in the Egyptian funerary texts. It can be translated as lock of hair or mourning and it is closely linked to the idea of destruction of evil, the healing of the lunar eye and finally recovering the Udjat eye.
S3mt seems to refer to something related to the mourning ritual and focused on the mourner’s hair. It could probably be considered as the hair that during the mourning rite women manipulated with a symbolic meaning, shaking it forwards (nwn sm3) or pulling it (nwn m swt).

Mourner making nwn m gesture of pulling her front lock of hair. Relief from the mastaba of Mereruka. VI Dynasty. Photo: Mª Rosa Valdesogo Martín.

Two women shaking their hair. Relief from the Red Chapel of Hatshepsut in Karnak. Photo: Mª Rosa Valdesogo Martín
The funerary texts communicate that this s3mt was cut, using the Egyptian word Hsq, which meant “cut”, but also “behead”. And also we find evidence that the mourners were shaved at the end of the mourning rite.
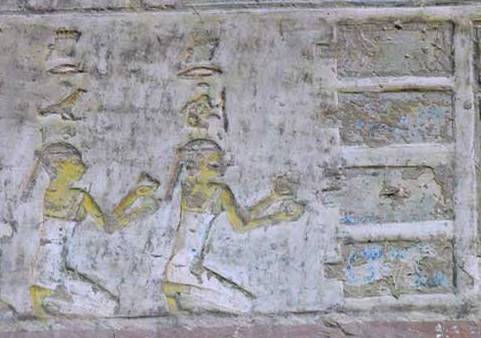
The two Drty (two kites), offering nw vases with short hair to the four pools. Relief from the tomb of Pahery in el-Kab. XVIII Dynasty. Photo: http://www.osirisnet.net
Many documents assimilate the hair s3mt with the s3bwt snakes. These were malign animals that in Egyptian mythology beheaded the gods, so they were an image of the enemy and responsible of the death.

Beheading the snake as an image of the evil. The cat of Heliopolis killing the snake Apohis, enemy of Re. Painting from the tomb of Inerkha in Deir el-Medina. XIX Dynasty. Photo: http://www.osirisnet.net
In Egyptian funerary belief, it is necessary to restore the head for living again and annihilate those s3bwt. Making that the adversary is wiped out; the gods recover their heads and also their faculties for seeing, breathing and knowing. In the funerary ambit, this will benefit the deceased, since cutting the s3mt will have the same effects on him: to recover the faculties that give him access to the new life.

Tekenu wrapped in a shroud and in foetal position over a sledge. Painting from the tomb of Ramose in Gourna.XVIII Dynasty. Photo: Mª Rosa Valdesogo Martín.
Cutting the s3mt is also closely related to the sacrifice and the figure of tekenu. This human victim, who goes back to ancient times in Egyptian history, has a double value, expiatory and propitiatory. In the first documents, one of the remarkable elements of the human victim is a front lock of hair. Once the human victim is replaced by an ox in the Opening of the Mouth ceremony again the lock of hair is one of the most important elements. So, this last one seems to be related with the evil elimination.

Sacrifice of an ox in the funerary ceremony. Painting from the tomb of Menna in Gourna. XVIII Dynasty. Photo: http://www.osirisnet.net
As cutting the s3mt is a way of removing the bad, it is also a way of recovering the Udjat eye as symbol of the final resurrection. Firstly Thoth spits on the damaged eye of Horus and this action is narrated in sacred texts as Thoth spitting on the hair sm3, afterwards the mourners are shaved or the s3mt is cut and the Udjat eye is offered to the deceased.

Eye of Horus, the falcon god. Detail from an image of Horus in the tomb of Roy in Dra Abu el-Naga. XVIII Dynasty. Photo: Mª Rosa Valdesogo Martín.
Summing up, to cut the s3mt supposes annihilate the enemy, the evil but also recover the Udjat eye and allow the final resurrection.







