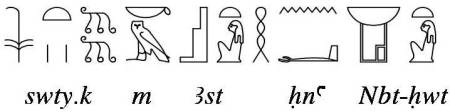
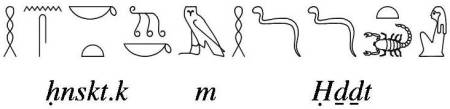
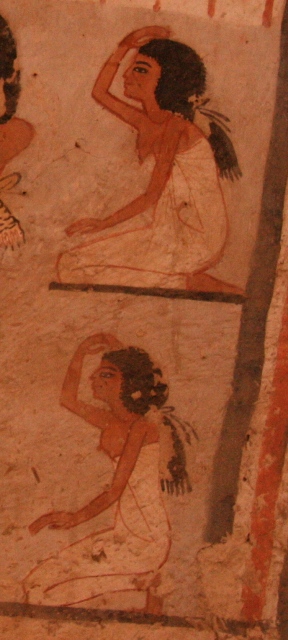Egyptian funerary texts and iconography mention the mourners in the role of Isis and Nephtys as making a mourning ritual with their hair for the benefit of the deceased. According to the sources, this rite was a part of the practises which formed the Opening of the Mouth for the mummy’s rebirth.
There is evidence of the Opening of the Mouth rite from texts of the Old Kingdom (inscription in mastaba of Metjen and in the Pyramid Texts). The Coffin Texts of the Middle Kingdom continue demonstrating the existence of this rite. In this period of the Egyptian history maybe can we envisage already one graphic proof in the stele of Abkaou (stele C15) from Abydos. In it the sculptor represented the rites of the Osiris festivity[1], where the myth was reproduced. The two mourners shake their hair over the corpse; between them we can see the hieroglyphs of the adze and the sledge. What does it mean?

Detail of the stele of Abkaou in the Louvre Museum. XI Dynasty. Photo: http://www.commons.wikimedia.org
The sledge is the phoneme tm; it can be a negative verb[2], but it also is the term for “to complete”, “be completed”, in the sense of uniting the different parts of the body[3], mainly in relation to the mummy limbs[4]. The adze could be the verb nwi “to be in charge of”[5]. So, we could read the inscription as “in charge of completing” in the sense of restoring the corpse of the deceased. That would not be crazy if we think that in the legend Anubis was the one who embalmed the body, but with the assistance of Isis and Nephtys.
However, looking at the entire register of the stele there is no trace of inscription in the other images. So, why do we have to consider these three hieroglyphs as an inscription?

Detail of the register with the Osiris festivities. Stele d’Abkaou. Musée du Louvre. XI Dynasty. Photo: http://www.commons.wikimedia.org

The tekenu on a sledge. Detail from the tomb of Montuherkhepeshef in Gourna. XVIII Dynasty. Image: http://www.excavacionegipto.com
If we consider them just as the pure objects that they represent, we notice that the adze is one of the main tools in the Opening of the Mouth ceremony in the New Kingdom iconography; on its behalf the sledge is one of the means for transporting the human victim/tekenu, whose ritual we have seen was also part of the Opening Mouth ceremony in New Kingdom.
One possible theory could be that in the stele of Abkaou the sculptor was representing the Opening of the Mouth ceremony and the morning ritual in a shorten version, as it was done later in the New Kingdom, when artist included in the same scene mourners, priests, corpse and ritual tools. And we could as well think not just of a short version, but a codified way of representing a hidden ritual in the attempt of protecting the information of a confidential rite.

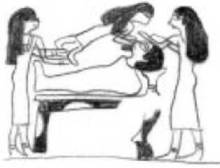
Opening of the Mouth ceremony. The image shows the two mourners, the priests and the table with all the utilised tools, included the foreleg of an ox. Painting from the tomb of Khonsu in Gourna. XIX Dynasty. Photo: http://www.osirisnet.net
The renovating rites for the mummy’s rebirth might be secret. All along this work we have read some funerary texts making allusion to this concept of “hidden” in everything surrounding Osiris’ death and resurrection. For instance, in the tomb of Ramsés IX the inscription accompanying the scene of the women pulling their frontal locks of hair says: “…they are mourning over the secret place of Osiris…they are screaming and crying over the secret place of the ceremony …they move away SnDt[6], their two arms with their two arms, their secret is in their fingers…”[7]. In the same line we have the coffin of Ramses IV, decorated with both mages of Isis and Nephtys pulling their frontal lock of hair and whose inscription says: “…the two goddesses who are in this secret place…they hide the secrets of the divine land… They move their faces during the moan; they mourn over the secret corpse… Both goddesses are holding their locks swt”.
It seems that in ancient Egyptian belief, the mystery of death and resurrection was not accessible to all people; because of that in the Book of the Dead we read in relation to the Osiris’ resurrection. “… it is a secret of the Duat and a religious mystery in the deceased’s Kingdom …it is a mystery, that cannot be know, to take care of the blessed heart, give him movement, take away the bandage from his eyes, open his face…Read that with no one seeing it, apart from your truly friend and the lector priest”[8].
The death itself was for the dead an initiation to the Hereafter’s mysteries[9]. Only the priests knew the secret of the Osiris death and resurrection, and to keep this secrecy was crucial for the universal harmony[10], possibly for that reason the “night of Isis” hid the mysteries of resurrection[11]. Even Isis sometimes received the name of “The Mysterious One”, since she “has been everything she has been, everything she is and everything she will be, and her veil, no mortal has never took off”[12].
The Theban Books of Breathing, dating from Ptolemaic period was a funerary text recited just before closing the cover of the coffin [13] and the woman in the role of Isis gave a speech for reviving Osiris and help his soul go up to the sky as lunar disc: “That is something that needs to be hidden. Do not let anyone read it. It is useful for one in the necropolis. He will live again successfully millions of times”[14].
The chapter 17 of the Book of the Dead mentions the moment Osiris recovers his virility thanks to Isis, and she stresses the secret nature of her action: “I am Isis, you found me when I had my hair disordered over my face, and my crown was dishevelled. I have conceived as Isis, I have procreated as Nephtys. Isis dispels my bothers (?). My crown is dishevelled; Isis has been over her secret, she has stood up and has cleaned her hair”
The Magical Papyrus Salt 825 contains a text about the rite for the conservation of life and it informs the reader that the “House of Life” is hidden, unknown and invisible; it is a “secret book…contains life and death. Do not reveal it, the one who reveals it will die suddenly or will be murdered”[15].

Opening of the Mouth ceremony at the door of the tomb. Painting from the tomb of Khonsu in Gourna. XIX Dynasty. Photo: http://www.osirisnet.net
Everything points to the idea that in ancient Egypt the resurrection process is something that only concerns to the deceased and the team helping him in his recovery and that it is not something accessible for everybody. That would explain then why there is no much iconographical evidence of the Opening of the Mouth ceremony; it comes mainly from New Kingdom on (tomb decoration or papyri) and it is not explicit at all. On the other hand these scenes showing the priests and mourner with the mummy in front of the tomb would not be real. If the ritual for the resurrection was something secret, the Opening of the Mouth ceremony could not be made in open air. All practices for helping the mummy to come back to life should be made inside the tomb or inside a special building in the necropolis. So the images of the mourners crying close to the corpse while the priests are officiating would be the artistic solution to allude to the rite without revealing details.
[1] Gayet, 1886, pl. LIV.
[2] Wb V, 302, 5.
[3] Wb V, 303.
[4] Wb V, 305, 1.
[5] Wb II, p. 220
[6] Fear (?).
[7] Piankoff, 1942, pp. 1-11; 1944, pp. 1-62; 1946, pp. 1-50.
[8] LdM, 148.
[9] S. Mayassis, 1957, p. 218.
[10] S. Mayassis, 1957, p. 42.
[11] Sinesio, Epist., XIII,v.s. 89; S. Mayassis, 1957, p. 65.
[12] Plutarco, De Iside et Osiride, 9.
[13] J.Cl. Goyon, 1972, p. 217.
[14] Book of Breathing I, 1.
[15] Ph. Derchain, 1964, p. 139.
[16] S. Mayassis, 1957, p. 40.