We have already seen how in chapters 107, 109, 332 and 533 of the Coffin Texts the moon is the main element. In them Hathor is the lunar goddess who guides the boat during the night (this boat assimilated to the quarter of the moon) and the one who receives the deceased in the Hereafter. Her two ringlets wprty are separated and/or given and this helps the dead to get out from the darkness of the death and see the Hathor’s face, that is, the moon, the light.

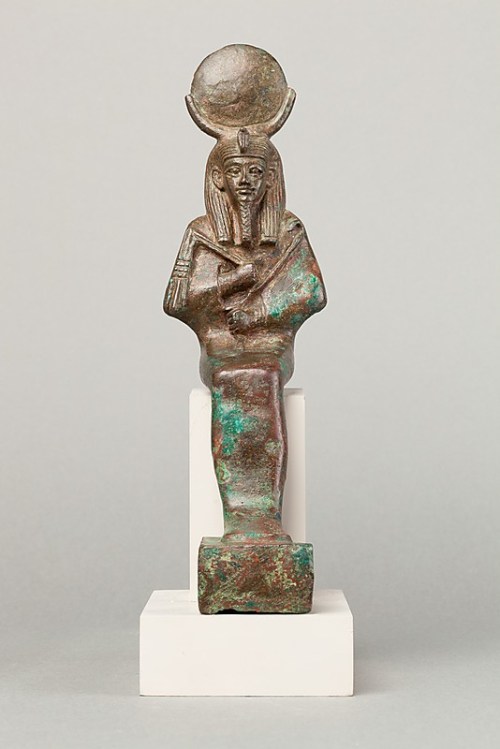
Image of Hathor with her two ringlets at both sides of the face. Paintign from the tomb of Roy in Dra Abu el-Naga. XVIII Dynasty. Photo: Mª Rosa Valdesogo Martín.
Hathor is “The one with bright face” (thnt Hr), « The Luminous one » (HAit)[1], and her two ringlets open to see « The Bright One, who makes live everyone she loves, people live when they see her » [2]. The idea of this act is completely opposite to the nwn gesture of covering the eyes with the hair; to die means a lack of light; it is the night of the death; the rebirth comes when the moon appears and provides light in the darkness.
Why is the moon so relevant in the deceased’s resurrection? It is a star that grows and dies, but the moon’s death is not definitive; after a period of some days it revives and appears again as a first quarter. The moon is at the same time death and resurrection, darkness and brightness. The moon is the first dead and symbolises the crossing point from death to life. For that reason the human being wants to have also a lunar nature; the star’s regeneration means a hope of resurrection for him.
Some cultures consider the moon the place for the resurrection; it can be as a trip in the star or as an immortal stay in it after the death. According to R. Briffault, in tribal societies, thanks to its cyclic nature, the moon measures the time and also creates it[3], so it has the mystery of the resurrection. The moon changes constantly, it increases and decreases, with an interval of invisibility (identified with the death), where it goes out from regenerating itself[4]. If the moon causes the time, to convert in moon means to control the temporality and come into the eternity.
Due to this changing nature, lunar mythic beings are usually crippled[5], as in Ancient Egypt was Osiris. The moon dies, as the man dies, and it resurrects as the man wants to resurrect. It is supposed the human condition to be identical as the lunar condition, so humans, after dying, come back to life in a lunar shape. For that reason for ancient Egyptians Osiris was “the moon in the sky”, he renews himself as he wishes and he gets old when he wants[6].
This context helps us understand the lunar nature of Hathor and why opening her two ringlets of hair means to get into the light, into the cyclic renewal, to get into the lunar boat and plough through the night sky[7]. Lunar Hathor guides the dead in the boat through the sky until Sothis, the morning star which announces the flood and the beginning of the Egyptian year, so the renewal of everything.
The ancient Egyptians celebrated the « Festival of the Sky » (Hb n pt), which inaugurated the lunar year and started with the appearance of Sothis. This moment was called in Egyptian “opening of the year” (wpt rnpt). This same expression meant also « the beginning of the youth », since rnpt was substantive of the verb rnpi (« to be young », « to be rejuvenated ») [8]. We find then two parallel concepts: the opening of the lunar year and the beginning of the lunar youth of the deceased. We must here remember that with the term rnp was also designed Osiris in the Songs of Isis and Nephtys.
The moon is a symbol of fecundity too , since it controls the waters, the rain and the tides[9]. Moon seems to be associated to the primeval waters as receptacle of creation power. For that reason the moon metaphorically speaking is the egg or the womb of the world, both elements as life generators. That makes the moon a life centre; and if it distributes the waters, it also intercedes between the sky and the earth (whose union we have seen is the hierogamy, the primeval couple).
In many cultures, the moon is closely related to woman and her fecundity power, because her physiological cycle is also regulated by the star. The moon is, then, the “Lord of the women” and he is sentimentally united to them. “Many people thought that the moon, with the look of a man or with the shape of a snake, mate with their women” [10], in the same way Osiris, as lunar god, is bound to Isis. The menstrual cycle contributes also to the idea of the moon as the first husband of female, as Osiris is Isis’ spouse.
As a star bound to the female fecundity, the moon is united as well to the Mother Goddess, and therefore has a maternal influence over the individual, as alimentary and affective mother[11]. In the funerary ritual that turns the deceased into a new born, who Isis looks after and Hathor takes in (both goddesses related to fecundity and moon).
On the other hand, the connection between the moon and the femininity would explain the intervention of the two mourners in the roles of Isis and Nephtys in the funerary ceremony for helping in the deceased’s resurrection. It would also explain why lunar Hathor, opening and/or giving her two ringlets wprty, allows the dead to get into the Hereafter and aim for a lunar regeneration.
[2] A. Mariette, 1875, VI, 33, 8.
[3] R. Briffault, 1974, p. 297.
[4] According to Frazer, due to this regenerating nature, for increasing something it has to be done during the crescent and for decreasing it during the waning moon. (J.G. Frazer, 1914, Vol. II, p. 133).
[5] G. Durand, 1979, p. 292.
[6] A. Mariette, 1880, II, 54 f., Z.5.
[9] G. Rossi, 1990, pp. 32-33.
[10] M. Eliade, 1970, p. 147.
[11] It is proven that there are more births during full moon (G. Rossi, 1990, p. 36).