The whole funerary ceremony is full of practices that recall the mythic death and resurrection of Osiris and the mourning rite is not an exception. The legend tells how the goddess Isis, when mourning the death of her husband, became a kite and put over the mummy of her husband; flapping her wings she could give the breath of life to Osiris and helped in his reanimation. In this work we have seen that there is also in the thought of ancient Egypt an assimilation between hair and feathers, therefore the nwn gesture of the mourner shaking the hair sm3 forwards the corpse could be interpreted as a way of producing the air that the deceased needs for breathing and coming back to life.

Isis as a kite flapping wings over the corpse of Osiris. Relief from the temple of Seti I in Abydos. XIX Dynasty. Photo: http://www.common.wikimedia.org)
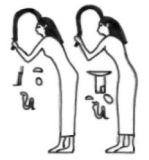
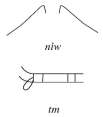
Changing into a kite, Isis could also restore Osiris’ virility. Egyptian funerary texts claim that when the mourners (smwt) give their hair sm3w to the deceased, he impregnates those women. It is interesting to notice that the Egyptian year started with the inundation (season of akhet), which was announced in some rituals (also the funerary one) with the nwn gesture, and the first month of that season was called, which means « inebriation ». On the other hand, the reduplicated form of txi is txtx and means “to dishevel”.

Isis as a kite is over the body of the dead. Statuette of prince Tutmosis, son of Amenhotep III. XVIII Dynasty. Altes Musuem (Berlin). Photo: Mª Rosa Valdesogo Martín.
Inebriation and dishevelling are two concepts together in the orgy, and this one is a way of coming back to the primeval chaos. It is the first state of creation, where sexuality and dishevelled hair take part. From anthropological point of view orgy is an act on behalf of life, it helps in generating a new productivity and in agricultural societies it strengthens the agrarian fertility; the orgy stimulates the renovation from the chaos. If the funerary ceremony is a way for getting the deceased’s resurrection through a return to the primeval moment, the eroticism, which encourages the chaos’ creation power, needs to be also a part of the ritual.
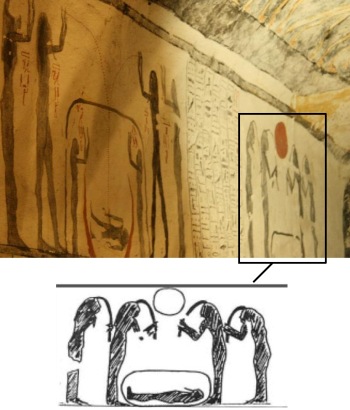
When the Egyptian mourner was making the nwn gesture during the Opening of the mouth ceremony, she was making a symbolic movement with her hair sm3 recalling the episode of the Osiris legend when Isis over the mummy restored the virility of her husband and copulated with him.

Opening of the Mouth ceremony; on the right the mourning is making the nwn gesture forwards the mummy. Tomb of Renni in el-Kab. XVIII Dynasty. Photo: http://www.osirisnet.net
The ejaculation of Osiris was a very important step in the myth because it was a proof of his physical regeneration; in fact the virility is in Egyptian sacred iconography a resource the artist had for indicating the resurrection, since he represented the deceased with “penile erection”. It also granted the conception of Horus, his heir, his avenger, the one who eliminated the evilness and restored the order, succeeding to the Egypt’s throne and allowing his father Osiris to revive as king of the Hereafter.