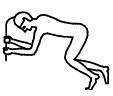
Iconography and texts point to an Egyptian funerary custom of shaving or cutting a piece of hair to the two mourners in the role of Isis and Nephtys. But, does the archaeology say something to us? The answer is yes. There is archaeological information from different moments of the Egyptian history proving the existence of hair offering to the dead.
- In the tomb of king Djer in Abydos (I Dynasty), a piece of hair and a false fringe were found by Petrie. He considered that they could be from the queen. Nowadays these remains are in Pitt Rivers Museum of Oxford[1]. In a common sepulchre in Abydos, dating possibly from the III Dynasty, many locks of hair were found, some of them were plaited and some were tangled up[2].

Hair remains from the tomb of King Djer. I Dynasty. Pitt Rivers Museum in Oxford. Photo: http://www.prm.ox.ac.uk
- In a “pan-grave” from the Middle Kingdom near Balabish[3], at the south of Abydos, was found a burial with a masculine mummy, close to the body were laying out some plaits of hair, which apparently did not belong to the mummy[4], so they should be a ritual offering.
- In the tomb of Tutankhamon was found inside a small anthropoid sarcophagus a plait of hair belonging to the Queen Tiye. According to A. Rowe, that would a queen’s relic, who was divinised, so that plait was considered a goddess’ hair[5]. Due that Queen Tiye was dead when Tutankhamon was buried, it seems much more logical to think of a familiar relic[6].
- From Deir el-Bahari is a group of tombs from XVII, XVIII and XIX Dynasties. Maspero assures there were locks of hair wrapped and put between legs, arms and around the necks of each mummy[7].
- In a tomb of Deir el-Medina were found locks of hair inside a basket[8].
- In the tomb of Queen Ahmose- Meritamun (XVIII Dynasty) H. E.Winlock found three baskets with human locks of hair and plaits of hair inside them.

Inner coffin of Ahmose-Meritamun. XVIII Dynasty. Cairo Museum. Photo: http://www.wikimedia.org
They were found with some other toilette objects. For that reason, Winlock considered that this hair was maybe for the Mertiamon’s hairdressing in the Hereafter[9]. This hypothesis sounds logical.
- In many houses from Amarna were found clay balls with hair inside. They cold maybe be utilised for some kind of domestic magic[10].
- In el-Kahun, Petrie found in 1890 in a tomb dating from the XX Dynasty two clay balls with locks of hair inside[11].
- From Deir el-Bahari is a mummy dating from XXI Dynasty of a young girl, between her two legs were put locks of hair of 40 cm long[12].
- In Gurob Tomb 605 at both feet of a female mummy was a squared case, which contained locks of hair. In some other tombs were also found hair remains[13].
- Finally, we have to mention the Douch necropolis, in el-Kharga[14] and dating from I-V centuries. In ten tombs were found deposits with globular clay vases with cut hair wrapped in clothing packs inside[15]; these vases were sometimes on the ground and sometimes inside a kind of whole in the walls of the funerary chambers . According to scholars the hair inside did not belong to the deceased ones, since these ones still had their own hair, but offerings.

The two Drty (two kites), offering nw vases to the four pools. Relief from the tomb of Pahery in el-Kab. XVIII Dynasty. Photo: http://www.osirisnet.net
All these archaeological remains make us think of those images of the twomourners called Drt with short hair at the end of the Opening of the Mouth ceremony and also of those texts mentioning the shaving of the mourners and the cut of the s3mt.
[1] Petrie and M. Flinders, 1902, p. 5, Pl. IV, fig. 7.
[2] Maspero, 1912, p. 170.
[3] It was in the group B 213, near the cultivable area.
[4] Wainwright, 1920, p. 11.
[5] Rowe, 1941, p. 624.
[6] Nachtergael, 1980, p. 243.
[7] Maspero, 1893, p. 274.
[8] Wagner et allii, 1984-1985, p. 188. They are in Musée du Louvre (Département des Antiquités Égyptiennes, Inv. Nº E 18851).
[9] Winlock, 1932, p. 34, Pl. XXXII y XXXIII.
[10] Peet and Woolley, 1923, p. 66.
[11] Crompton, 1916, p. 128. They are in the Manchester Museum.
[12] Daressy, 1907, p. 34.
[13]Bell, 1985, pp. 61-86, Pl. II.
[14] Dunand, Heim, Henein, Lichtenberg, 1992; Wagner et allii, 1984-1985, pp. 175- 202.
[15] The tombs are: T3, T4, T5, T7, T9, T11, T12, T53, T58, T66.